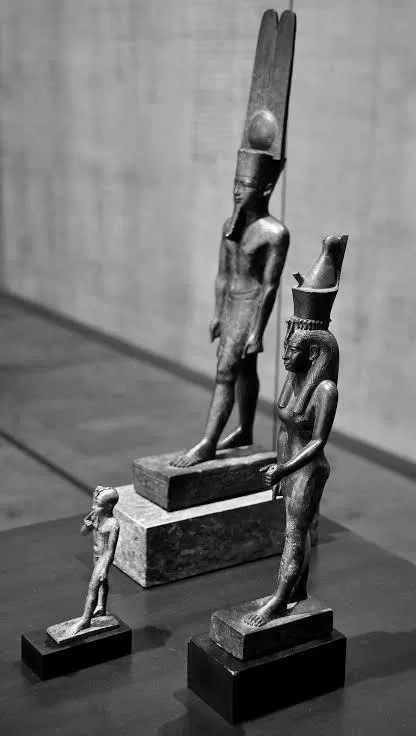
The Egyptian God Nut is one of the oldest deities in history. His lore dates back to the founding of the city of Heliopolis during the Predynastic period, 3100 BC. Initially, Nut was considered the goddess of the nighttime sky but later became all-encompassing, embodying the entire ‘heavenly’ atmosphere.
Khonshu was a scribe.
Khonshu is a fictional god created by Doug Moench and Bill Sienkiewicz to represent the Egyptian deity Khons. This God of time and the moon is a changeable Egyptian deity with benevolent and demonic attributes. His role in ancient Egyptian mythology is unclear, but he has been attributed to protecting the night’s residents.
Khonshu was an Egyptian god associated with several gods and goddesses, including Ra and Shu of Thebes. Other gods associated with Khonshu included the moon and sun. In some versions, Khonshu is portrayed as a bloodthirsty deity who eats other gods. In the New Kingdom, Khonshu was seen as a more gentle deity.
Although his role in the film is unclear, Khonshu’s appearance and personality are reminiscent of comics. In the comics, Khonshu and Spector have an oscillating relationship. In the comics, they have a mutual dislike for one another.
Aten was a god of writing.
The God of writing, Aten, was associated with writing. In his third year of regnal rule, Akhenaten enclosed the didactic name of Aten in a cartouche. He then carried out an extensive “Aten-project,” reorganizing religion, art, cult administration, and the economy. He also sent his high priest Amun into the desert to reform his priesthood.
In the Amarna religion, Aten and the Pharaoh were closely related. The Pharaoh performed signs and wonders and intervened in individual destiny. The Pharaoh was a superhuman power during the Old Kingdom, as he was the Great Father of the World.
In his reign, Akhenaten emphasized the visible aspects of religion. He also removed the seal of royal approval from the old religion. This caused massive trauma in Egypt and made the God of writing primarily forgotten for 80 years. The development of modern Egyptology followed his reign. Ultimately, the Aten project failed.
Amun was a god of obscurity.
Amun was the God of air and wind, and the name means “the hidden one.” This God was worshiped as the unknowable but was highly regarded by the Egyptians. During the Middle Kingdom, Amun was part of the Theban Triad and was associated with the sun god Ra. In addition, Amun was associated with the color blue, the color of the sky seen through the air.
Amun was worshiped in places outside of Egypt, too. In Nubia, he was known as Amane. He regulated the government of the Nubian people, with priesthoods choosing kings and directing military expeditions. God was considered to be everywhere and lord of all.
Before the rise of Ramesses, Amun was a minor god. However, over the centuries, his role was expanded. He rose to become a significant god and the chief of the gods during the Middle Kingdom. By the New Kingdom, he was regarded as a national god.
Ptah was a god of war.
Ptah is one of the oldest deities in Egyptian mythology. He was the creator of the universe, the husband of the goddess Sekhmet, and the God of war and craftwork. He was also identified with the Greek God Hephaestus. He is depicted in various artistic depictions, including a mummy-like image. His temple is located in Memphis.
He was often depicted as a handsome deity, wrapped in cloth like a mummy with his hands-free to hold his staff. His hair was shaven, and he wore a skull cap. Fashion in ancient Egypt was very different from what it is today. Ptah was also the High Priest of the temple in Memphis and had the title of Great Leader of Craftsmen.
Ptah’s statues are also imposing, depicting him as a giant bearded man with four feathers on his head, a robe, and a lance or spear in his hands. Sometimes, he is accompanied by a lion-headed god, representing divine strength.
Isis was a goddess of fertility.
Isis was an Egyptian goddess of fertility and was worshiped as such. Isis became the most important Egyptian God in the Middle Kingdom, and her temples began to spread throughout Egypt and the surrounding region. Her temple at Philae was one of the Egyptians’ and Nubians’ most important religious centers. Isis was believed to have a magical power beyond that of other gods. She was said to protect her kingdom from enemies and rule over the skies and the natural world. She was also believed to control fate.
Egyptian priests served the Isis cult. The priests were both male and female. Many priests of Isis were healers. Priests had many special powers, and many believed that the knots they tied had special forces. Isis’ symbols included a throne headdress, a crescent moon disc with cow horns, the sycamore tree, and a kite hawk with outspread wings.
Many women in ancient Egypt worshiped Isis as a fertility goddess. In addition to fertility, she was the goddess of magic, and people turned to her for spells to help them solve their problems. According to myth, Isis tricked Ra into telling her his secret name and gained several magical powers. Her son, Horus, was conceived through magic and was her only child. Many historians speculate that Isis may have inspired the Virgin Mary of the Christian Bible.
Horus was a god of magic.
Egyptians worshiped Horus, a deity associated with the sky. He was the son of Isis and Osiris and was tasked by his mother to protect Egypt. His father, Osiris, was killed by the God of the desert Set, but he survived and fought Set to restore Egypt. This war led to the fall of Set’s empire, and Horus was chosen as the new ruler of Egypt. During his reign, he became associated with Lower Egypt and became its patron.
Horus was the most important Egyptian God during the Middle Kingdom. He was initially associated with the sky and the sun. He was the son of Osiris and Isis and the brother of Set and Nephthys. He was also a god of healing, and Egyptians would invoke his name during prayer for protection when hunting. Egyptians also believed he had a protective influence over predatory and wild animals.
The name Horus comes from the word “distant.” The image of Horus represented the sun, the moon, and the last edge of the earth. The sun’s appearance also represented a chance for worshippers to reflect on the character of God.
Ammit was the god of the moon.
Ammit, the Egyptian God of the moon, was a powerful god who could judge the souls of the dead. Ammit would cast unworthy souls into a lake of fire. Scholars say this represents the concept of destruction. In ancient Egypt, Ammit was worshipped to ward off evil.
Ammit was a god of balance and order but also had harmful purposes. He is often depicted beside the scales of Ma’at in the Underworld. Ammit’s negative qualities are reflected in his depiction in Marvel comics. His primary purpose is to devour the impure heart, and this would be similar to Moon Knight’s aims.
The Egyptian God Ammit is also featured in Marvel comics. In the first episode of the Moon Knight series, Ammit appears as an avatar of Arthur Harrow, who was granted the power of God to form a devotee.
Anubis was a god of the sky.
The Egyptian God Anubis is best known for his relationship with the God Osiris, whom he conceived from the goddess Isis. In addition to his close relationship with God, he also adored Isis. As a result, the Egyptians believed he would protect them from harm and help them achieve peace and harmony. He was also supposed to have the power to protect their children and help them achieve their goals in life.
Anubis was also associated with death and mummification. His image often featured a man with a jackal head. His body was typically black and often depicted in a seated position. In addition, many people believed that he would protect them from illness and battle. His name comes from the word “anupu,” which means “to sacrifice.”
Anubis was also considered an essential god of mummification, and priests often wore his mask during the mummification ceremony. Some ancient Egyptians even believed that the Pharaoh was a living version of Horus. The Egyptian gods had a fascinating list of names, which were all intriguing.