There are many myths and legends associated with a Chinese deity scholar incense burner. In this article, we’ll discuss the shape of the burner, how it burns incense, and the legend surrounding Li Tieguai’s incense burner.
Legends of Li Tieguai’s incense burner
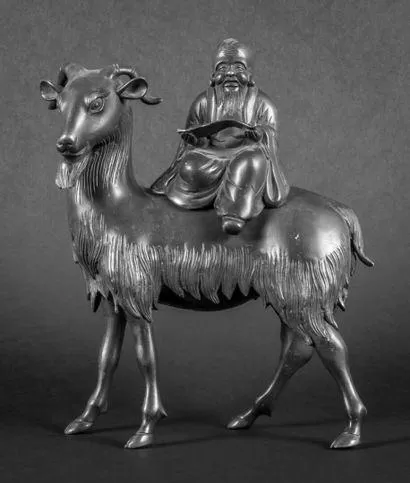
Legends of Li Tieguai relate to a Chinese deity scholar who is often portrayed as an old beggar with an unkempt beard and a large iron crutch. Although he is known to be irascible, he has a compassionate heart and helps those in need by dispensing medicine from a gourd bottle. As the first of the Eight Immortals, Li Tieguai embodies the Daoist archetype.
The image of Li Tieguai is often on the top of the incense burner. This Chinese deity scholar is one of the Eight Immortals and an important deity of the Complete Realization sect of Taoism. His soul is believed to have traveled to the island of Laozi after his death. His student, however, had a family emergency and could no longer keep watch over his body. Eventually, Li Tieguai returned to a burned-out body and took the body of a beggar who had just died.
The legend of Li Tieguai explains how this scholar became immortal. He lived during the Tang dynasty and was a disciple of Laozi. He was a master of alchemy, a healer, and a diviner. He received his divinity on the 23rd day of the 11th lunar month. He sometimes carried a cylindrical drum, presumably to aid in divination or ward off evil influences.
The Chinese deity scholar Li Tieguai’s Chinese incense burner has eight different symbols. Each one is representative of a different aspect of the deity. In addition to the eight deities, the gourd represents science, magic, and immortality.
The throne seated on the brush pot also features a rebus for luck, as it sounds like “luck.” A servant sits on Shoulao’s throne, tending to the tripod incense burner. Another incense burner depicts a long-tailed turtle sitting on a pine tree.
Shape of the incense burner
The shape of the Chinese deity scholar incense burner reflects its religious significance. It is topped with an image of Li Tieguai, one of the Eight Immortals and important deities in Taoism’s Complete Realization sect. Li’s soul was said to have traveled to Laozi after he died. He was supposed to be accompanied by a student who would take care of his burning body, but this student had a family emergency and died, leaving Li’s body unattended. He returned to his body and took the body of a beggar who had recently died.
The incense burner has a long history in China. It has been a part of spiritual traditions for thousands of years and gives off a very pleasing aroma. The shape of the burner is often based on the traditional Chinese Ruyi shape, with a meandering lotus pattern.
The Chinese culture of incense produced a wide range of artistic objects. Some of the earliest examples of incense burners were found in ancient China. Using ‘lu’, a Chinese word for ‘hill censer’, they were universally used in liturgical practices, divination, and rituals. In Chinese culture, the ‘hill censers’ had an important role in worship and were linked to ancestors. Some bronze burners were even constructed in the form of miniature mountains.
Incense burners can burn either stick or cone incense. The burning of the incense produces a smoke that can be used to purify the air, relieve stress, and promote relaxation. The smoke from incense can also serve as an insect repellent and a deodorant. Violet incense, for example, is considered to bring good luck.
Incense smoke is composed of particulate matter and gas products. The particles in incense smoke are not harmful to the human body, but there is evidence to suggest that incense smoke may be a cause of respiratory symptoms. However, these studies have not been conclusive enough to conclude that the incense smoke caused any health problems.
Purpose of burning incense
This incense burner is made of porcelain and features a dragon’s pedestal and a row of lotus petals that form a double pentagon. The top row of petals is the broadest, and the bottom row is the narrowest. The bottom row features a convex fold that connects the stem and bowl. The dragon’s legs form a right triangle and provide support to the bowl.
Incense consists of aromatic substances that release a fragrant smoke when burned. It is used in many cultures and religions as a form of sacrifice and communication with spiritual entities. It also purifies the air and is often burned in connection with temples. The main plant used for incense is the Cupressus funebri, though other species are also used.
The iconography of the incense burner is complex and there is no consensus on its interpretation, but most scholars agree that the overall layout of decorative elements is meant to represent the philosophy of yin and yang. The dragon symbolizes the yang, while the phoenix represents the yin.
Throughout Chinese history, incense burners have been used as religious symbols. Many people view them as sophisticated and symbolic representations. Some people think of a deity scholar incense burner as a companion for a Chinese deity. A Chinese deity scholar incense burner will have a lion-like appearance, and the lion is believed to have powerful mythic protective powers.
The use of incense is widespread throughout the world. In China, it is particularly widespread in the southwest. In Shaxi, for instance, incense is often used to communicate with spiritual entities, as well as to strengthen self-awareness. Some of these plants are used as medicinal plants or hallucinogens, but many of them are used for their fragrant smoke.