The question of which deity commonly represents the abstract principle of the heavens is important in popular mythology. The abstract concept of heaven is a central theme in many religious traditions. It is also commonly associated with the idea of good and evil. This article explores how the abstract principle of heaven is depicted in different religious traditions.
Al Haqq
In Islamic teachings, Al Haqq (the truth) is a universal principle that equates Allah with absolute truth, which is always eternal. This abstract principle suggests that Allah is separate from humanity and is inherently perfect, but also indicates that it is immanent within the world.
San-Juan
San Juan is a Chinese concept that commonly represents the abstract principle of heaven. It symbolizes eternal life and a universal source of joy and happiness. It has many different meanings in Chinese culture. San Juan is also used in popular culture to represent the heavenly sphere.
Hindu
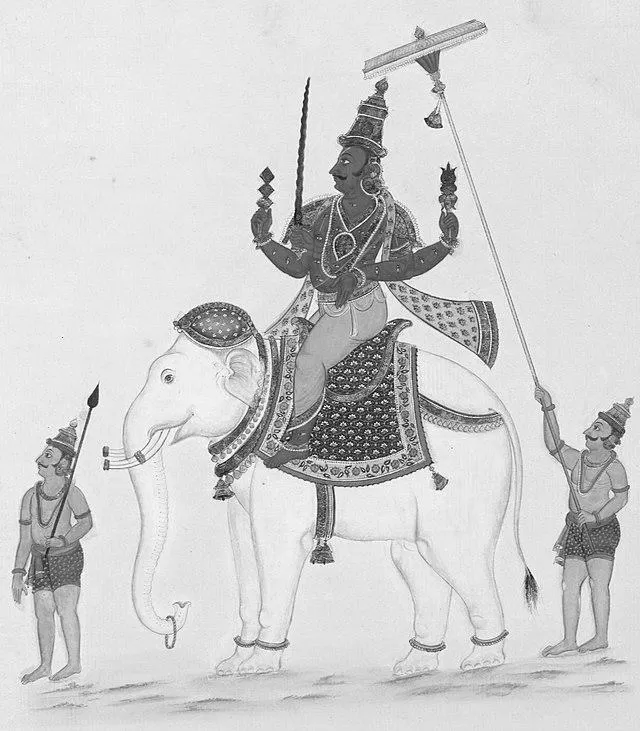
The Hindu deity is an abstract concept. It is a polymorphic concept. This means that each individual has several different personalities, each with specific attributes. Hindus worship several deities to satisfy their needs. One of the most important deities is Vishnu, the lord of heaven.
Other Hindu deities include Shakti and Shiva. Shakti is Shiva’s mother and is worshiped as the bringer of change and a manifestation of the feminine principle. She is often associated with knowledge, wealth, and might. The Shakta sect of Hinduism reveres Shakti as the Supreme Being.
The Hindu deity is often depicted as a personal god in popular culture. Many Hindus believe in the samsara cycle of rebirth, which continues until a person realizes their divine nature. This concept is also found in movies and television shows.
The Hindu religion has several deities, and the Hindu deity Shiva is one of the three most popular. Shiva is responsible for siring the other two Hindu gods, Ganesha and Karthikeyan. Shiva’s consort Parvati is also known as the goddess Kali, and she fights the evil Asuras. The God Shiva is portrayed as a limitless and transcendent entity in popular culture. The Hindu religion also has a cyclical view of creation and dissolution.
Fire is a critical element of Hindu culture. It is a significant element in yajnas. In ancient Hindu mythology, the goddess Agni symbolizes fire. Agni is the divine mediator between divine beings and humans, accepting sacrifices to worship the Hindu gods.
Buddhist
Buddhism commonly represents the abstract principle of heaven in various ways, including as an abstract concept and a material object. In many Buddhist traditions, the abstract code of heaven is represented by the bodhisattva, which is a Buddhist concept that focuses on the nature of the universe. In some practices, the idea of heaven is represented by kami, the image of a god in a material world.
Buddhism traditionally focuses on the individual over the group. The Buddha’s followers developed a theory that human beings are made up of processes such as physical sensation, perception, consciousness, and mental constructions. These processes are constantly changing and are subject to karma. Buddhist practice aims to realize the end of these processes or Nirvana. The concept of Nirvana is more abstract and can be described as a state of being free of worldly bonds and attachments.
Buddha’s teachings emphasize the importance of understanding the roots of our suffering. This is because suffering in life is caused by attachment. Among these causes are the desire to live and the thirst for material objects. Attachment to these things, or karma, is a significant source of suffering.
The Buddha taught four noble truths. These include the causes of suffering and how to stop it. He advocated the Eightfold Path, a path of wisdom. The Eightfold Path involves various steps to attain the state of Nirvana. Monks and laymen can follow these steps, referred to as “prajna” or “wisdom.”
The Buddhist doctrine is divided into three primary schools. The Dharmaguptaka is one of the three leading schools, along with the Theravada and the Mulasarvastivada schools. The Dharmaguptaka emphasizes the merit of devotion to stupas, which often depicts the Buddha as a bodhisattva in his previous life. The Dharmaguptaka also views the paths of sravaka and bodhicitta as separate and distinct.
Christian
The abstract concept of heaven, or heavens, is often represented as a white man with two eyes. The idea is widely accepted by Christians and is the basis for many beliefs. God is believed to be the creator of all things and that His Son Jesus was sent to the earth to save humanity from sin. The Christian Godhead consists of three members: the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.